It is estimated that only 20% of the US population is getting enough magnesium. There are several reasons why this number is so low, including a diet lacking in whole foods, as well as an increase in chronic illnesses that deplete magnesium from the body. Add to that the fact that most blood panels test blood serum (bloodstream) for magnesium even though depletion begins in the blood cells (the majority of magnesium is in your cells, not blood serum). Therefore, you can be deficient in your blood cells, but still test within the normal range in your blood serum and not even know that there is a deficiency.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in many daily functions. It is a co-factor for several enzymes. It is a necessary part of energy production, protein synthesis (making protein), muscle contractions (including bowel movements and digestion), cell signaling, and proper immune health. Magnesium also helps keep bones strong, regulates blood pressure, and aids in inducing sleep.
Magnesium deficiency can increase the risk of:
- Cardiovascular disease (heart disease)
- Osteoporosis
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Muscle cramps, including migraines
How Much Should Be Consumed?
The US recommended daily allowance (RDA) for an adult is between 310-420 mg of magnesium daily however, those with issues that hinder the ability to absorb magnesium may have to resort to higher amounts. Remember, that everyone may need different amounts in order to be in optimal health.
Things to consider in order to determing if you are absorbing enough magnesium in your diet include:
- Are you taking supplement high in zinc? Zinc supplements can interfere with the absorption of magnesium.
- Are you getting enough vitamin D? Magnesium absorption is partially dependent on vitamin D.
- Are there any disorders causing the body to excrete magnesium? Gastrointestinal, renal, or endocrine disorders can affect the body’s ability to maintain proper amounts of magnesium.
Ways to incorporate magnesium-rich foods:
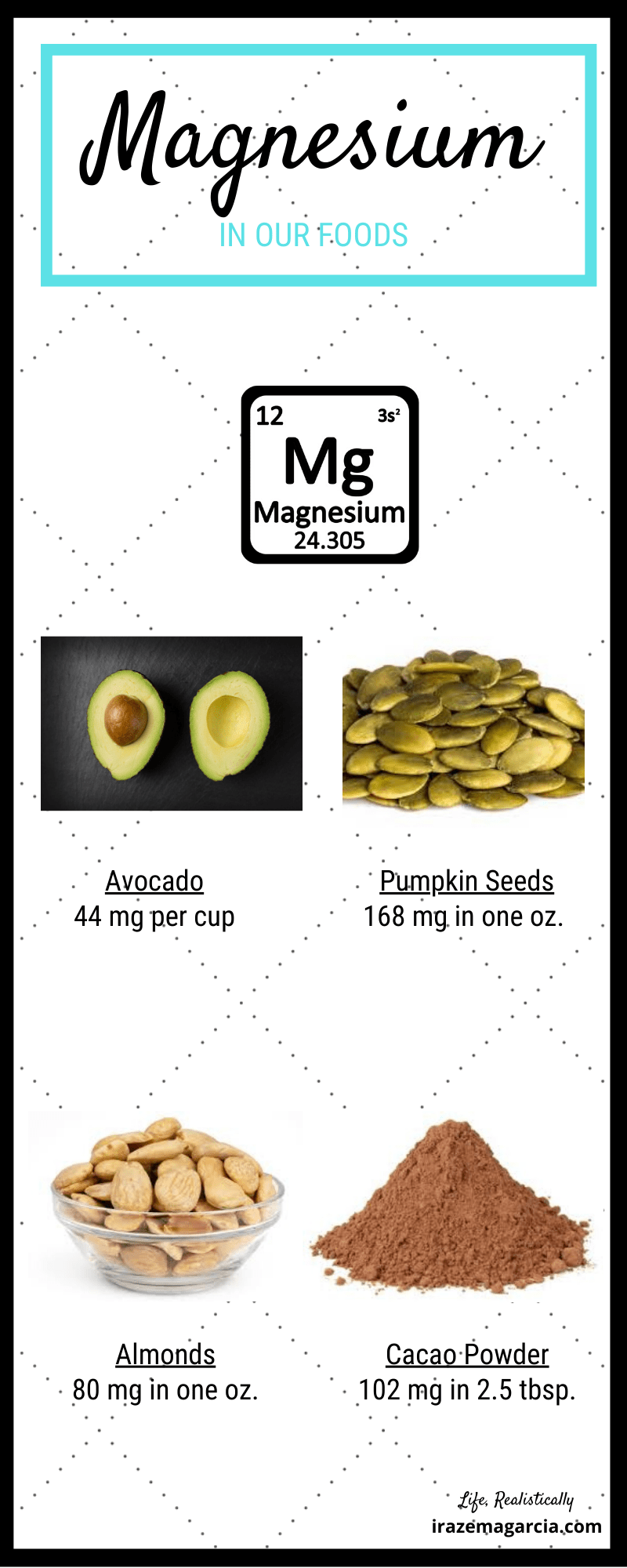
- Avocado (44 mg per cup): mash into a delicious dip or use as a garnish on top of soup.
- Pumpkin Seeds (168 mg per 1 oz. serving): toss on top of salads or incorporate into trail mix.
- Almonds (80 mg per 1 oz. serving): satisfy your sweet tooth and get a serving of magnesium with this almond hot chocolate.
- Cacao Powder (102 mg per 2 ½ tablespoon serving): add to a mocha smoothie or chocolate hazelnut chia pudding.
–Progress, Not Perfection–
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/15650-magnesium-rich-food
https://www.eatthismuch.com/food/nutrition/raw-cacao-powder,503803/

